


Emergency Rescue Vehicle Standards Everyone Should Know
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-06 Origin: Site









Emergency rescue vehicle standards have strict rules for design, equipment, and how fast they respond. These rules make sure each vehicle works safely and well in emergencies. Following these rules helps save lives. For example, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) has important benchmarks. Faster response times help more people survive:
NFPA 1710 Benchmark | Description | Impact on Survival Rates |
|---|---|---|
Call Processing Time | ≤ 64 seconds | Faster dispatch helps more people survive. |
Travel Time | ≤ 240 seconds | Saving each minute helps more people live. |
A good emergency rescue vehicle, like ones from CJQC, meets these main standards. These vehicles help first responders during important times.
Key Takeaways
Emergency rescue vehicles have to follow strict safety and performance rules to keep crews safe and help save lives in emergencies. Strong vehicle design, like tough frames and modular interiors, helps rescue teams work faster and stay safe in any situation. Special lighting, sirens, and warning systems help clear traffic and lower crash risks for emergency vehicles. The right equipment and good communication tools help medical and fire teams respond fast and do their jobs well. Regular maintenance, operator training, and following new rules keep emergency vehicles ready and crews safe all the time.
Why Emergency Standards Matter
Public and Crew Safety
Emergency response vehicle standards keep people and crews safe. Many injuries can happen during rescue work. Some main causes are:
Car crashes, especially at busy roads.
Getting hurt by loose things inside the vehicle.
Not wearing seat belts, which makes injuries worse.
Violence and attacks during emergency medical help.
Slipping or falling on wet or rough ground.
Modern emergency vehicles, like the Medical Diesel Cancer Screening Bus and V80 Short Shaft Running Ambulance, help lower these dangers. They have strong frames made with tough steel and special materials that soak up crash energy. These parts help keep people safe if there is a crash. Door beams and crumple zones protect the inside and spread out crash forces. New safety systems, like Electronic Stability Control and Automatic Emergency Steering, help drivers stay in control and avoid sliding.
These vehicles also help stop infections and meet world safety rules. Special driver lessons and better vehicle design help stop crashes. Giving drivers the same vehicle and using backup cameras help them see better and avoid accidents. All these things make emergency vehicles safer for everyone.
Effective Emergency Response
Emergency vehicles must be fast and work well. The Medical Diesel Cancer Screening Bus can quickly check and find health problems while moving. This helps emergency medical teams in cities and the countryside. The V80 Short Shaft Running Ambulance moves patients fast and gives good care on the way.
Built-in medical tools and live communication systems help teams act fast in emergencies. Fast driving and GPS maps help teams get to disaster areas quickly. These vehicles can give important care and checks in faraway places, helping many types of emergency vehicles.
By following strict rules, emergency vehicles help both patients and workers. They help emergency medical teams and make sure rescue crews can act fast and safely in any emergency.
Emergency Rescue Vehicle Design
Structural Integrity
A strong emergency rescue vehicle needs a tough frame. Engineers make these vehicles to handle crashes and rough roads. They use strong materials like high-strength steel and aviation aluminum. Polypropylene is also used because it is tough. These materials help the vehicle stay safe in hard conditions. They can resist heat, impacts, and rust.
International rules help companies design and test these vehicles. Some important rules are:
SAE rules for crash safety and equipment mounting.
The U.S. KKK-A-1822 rule for ambulance design.
NFPA 1917 and CAAS Ground Vehicle Standard (GVS v1.0) for keeping people safe and gear secure.
These rules say vehicles must pass crash tests and have strong seat belts. Medical gear must be stored safely. Groups like NIOSH and NIST help make these rules. They make sure every emergency rescue vehicle keeps patients and crew safe.
CJQC vehicles are known for strong frames. They have roll cages and high roofs to protect people inside. The Datong V90 Monitoring Type has a strong frame and good safety systems. It can drive off-road and handle sudden bumps. This makes it good for disaster areas.
Note: A strong emergency rescue vehicle can save lives. It keeps people safe during crashes or in dangerous places.
Accessibility and Durability
Rescue teams need to get to their tools and patients fast. Good design helps them do this. CJQC vehicles use modular customization. Teams can change the inside to fit each job. Shelves, trays, and panels help organize gear. This lets teams grab what they need quickly.
All-terrain features help these vehicles go where others cannot. High ground clearance and four-wheel drive help a lot. Strong engines let CJQC vehicles cross floods, rocks, and mud. This means rescue teams can help people anywhere.
Here is a table with some important durability standards:
Durability Aspect | Requirement/Standard |
|---|---|
Materials | High-strength polypropylene or aviation aluminum; impact, heat, and corrosion resistant |
Waterproof Certification | IP67: No water enters after 30 minutes at 1 meter depth |
Impact Resistance | IK08: Withstands high-intensity impacts |
Temperature Range | Works between -30°C and 70°C |
Extra Features | Shock resistance, modular design, and environmental adaptability |
Modular customization has more good points:
Teams can switch gear for different emergencies.
If a vehicle breaks, they can move rescue modules to another one.
Vehicles can be set up for special jobs, like wildfire response or medical checks.
Modular parts save money because teams can use them again.
CJQC emergency rescue vehicles meet these tough standards. Their design helps rescue teams work faster and safer, no matter where they are.
Safety Features in Emergency Response Vehicles

Lighting and Sirens
Lighting and sirens are very important for emergency vehicles. They help clear the road and warn other drivers. Every country has rules for how these work:
Blue lights mean there is an emergency. Only trained drivers use them when it is urgent.
Red lights are easy to see during the day. Blue lights are better at night. Amber lights show the vehicle is there but do not let it go first in traffic.
Flashing red lights warn people when the vehicle has stopped.
Lights must be put on the roof, in the middle, and on the dashboard. This helps everyone see them from all sides.
Sirens must be loud enough to be heard through thick car windows. Most emergency vehicles use sirens that are at least 200W. The speakers point forward.
Low-frequency sirens help drivers notice the vehicle if they do not hear the normal siren.
Using lights and sirens the right way helps emergency teams get to emergencies fast and safe.
Crash Protection
Crash protection keeps people inside the vehicle safe. New vehicles have special systems to stop crashes and lower injuries:
Automatic Emergency Braking can stop many rear-end crashes.
Forward Collision Warning tells drivers before a crash can happen.
Lane Assist and Blind Spot Monitors help drivers see what is around them.
Automatic Emergency Calling gets help after a crash and sends the location.
Night Vision and Alertness Monitoring help drivers see dangers and stay awake.
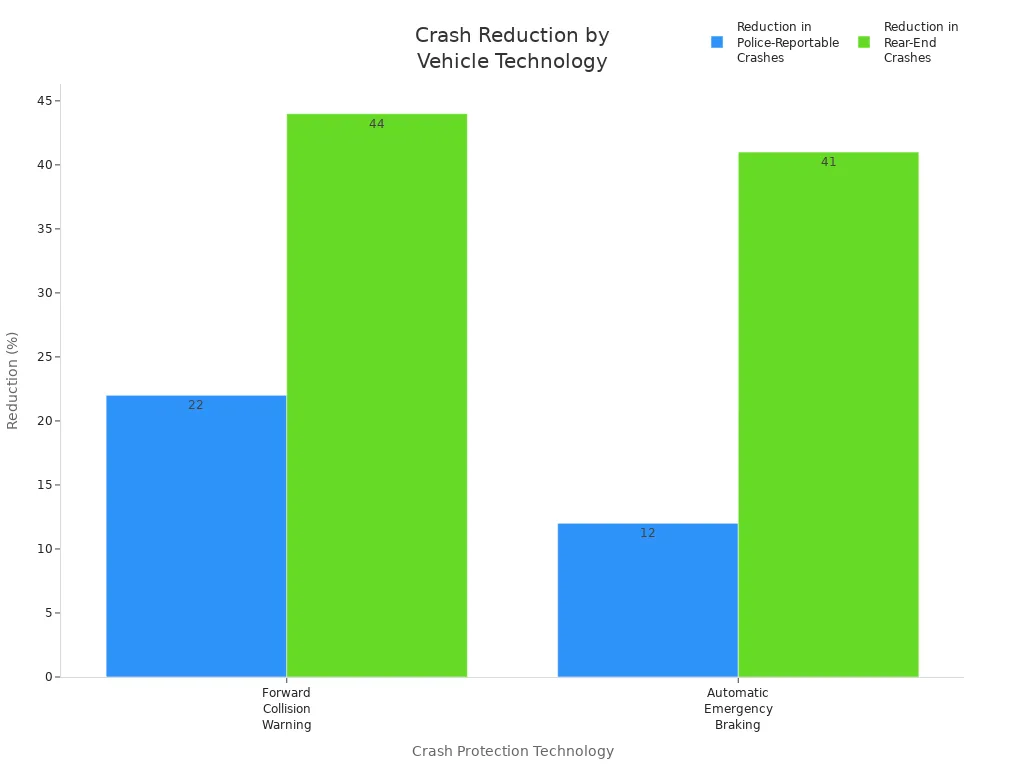
These systems, along with strong frames and safe storage for gear, make emergency vehicles safer for everyone inside.
Warning Systems
Warning systems help keep emergency crews and the public safe. New vehicles use digital alerts and V2X communication to warn other drivers:
Feature/Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Early Digital Alerts | Warns drivers 20-30 seconds before the vehicle comes. |
V2X Communication | Shares information between emergency vehicles and other cars. |
Audible and Visual Warnings | Sends alerts through car screens and beeps. |
Safety Cloud Platform | Sends alerts and works with navigation apps. |
Collision Risk Reduction | Makes crashes less likely by up to 90% compared to old lights and sirens. |
Move Over Law Support | Reminds drivers to slow down and move over for emergency vehicles. |
These systems help drivers react early, even if they do not see or hear the siren. They also help traffic move better and make sure emergency teams get there safely and on time.
Equipment for Ambulance and Fire Truck
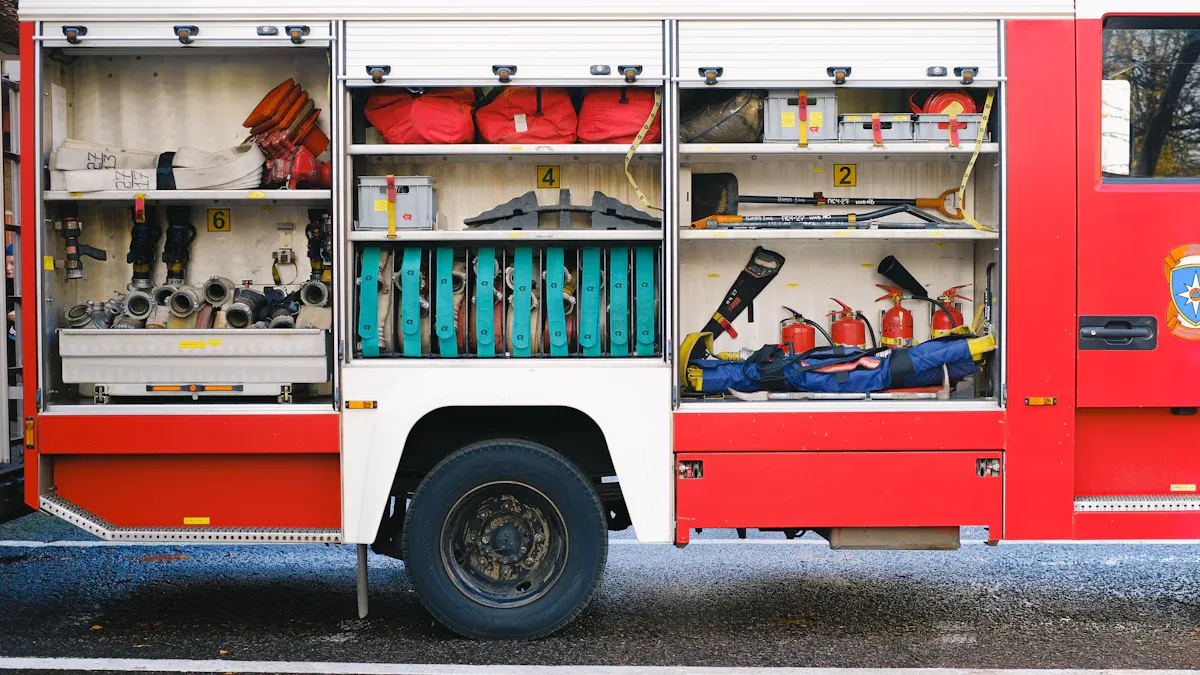

Medical and Rescue Gear
Ambulance and fire truck crews need special tools to help people and protect things. Each fire engine brings many tools for different emergencies. Having the right tools helps teams act fast and stay safe.
Fire trucks and fire engines must have strong pump systems. These pumps move water from hydrants or tanks to hoses. This helps firefighters put out fires. Most fire engines have a main pump, backup pumps, and small pumps for hard places. The Datong V90 rescue engine has a big pump that works well in disasters.
Firefighting tools on a fire truck include hoses, nozzles, and foam systems. Fire engines also carry ladders, axes, and hydraulic rescue tools. These tools help crews reach trapped people and break things if needed. Fire trucks often use thermal cameras to find hot spots and hidden fires.
Ambulance teams need medical tools to care for patients. Every ambulance has oxygen systems, defibrillators, and monitors. The CJQC mobile clinic has a portable colposcope, color Doppler ultrasound, and a biopsy refrigerator. These tools help teams find and treat problems quickly.
Rescue gear on a rescue engine includes stretchers, splints, and trauma kits. Fire engines also bring protective gear for crew safety. All gear must be stored safely to stop injuries while driving.
A normal checklist for fire trucks and ambulances looks like this:
Equipment Type | Fire Truck/Fire Engine | Ambulance/Rescue Engine |
|---|---|---|
Pump | ✔️ | ✔️ (for rescue engine) |
Hoses & Nozzles | ✔️ | |
Firefighting Equipment | ✔️ | |
Medical Devices | ✔️ | |
Oxygen System | ✔️ | |
Rescue Tools | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Stretchers | ✔️ | |
Ladders | ✔️ | |
Thermal Camera | ✔️ | |
Protective Gear | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Note: Storing equipment the right way and checking it often keeps everything ready to use.
Communication Systems
Good communication is very important for ambulance and fire truck work. Real-time systems let teams share information right away. These systems connect fire engines, rescue engines, and ambulances with command centers and other groups.
Modern fire engines use two-way radios, satellite phones, and mobile data terminals. These tools help teams talk, send texts, and share data. The Datong V90 rescue engine has GPS and CAD systems for live maps. This helps crews find the best route and avoid danger.
Fire trucks use alerts on many channels to reach all team members. Geo-targeting sends messages to the right areas and helps use resources better. Dashboards help command staff watch every fire engine and ambulance at all times.
Ambulance teams use safe communication platforms to protect patient information. These systems follow rules like HIPAA and NIST. Real-time updates help teams change their plans as things happen. Two-way communication lets responders send and get updates, which helps them make better choices.
Fire trucks and fire engines must keep working even if networks go down. Safe platforms keep teams talking when main networks do not work. Training with these systems makes sure every crew member can talk under stress.
Tip: Good communication helps teams work faster and keeps everyone safer.
Compliance and Training
Regulatory Standards
All fire departments must follow strict rules for safety. The nfpa makes the main rules for fire truck design and use. These nfpa rules help keep firefighters and people safe. The EPA changed rules for heavy-duty diesel vehicles in recent years. These changes let fire truck makers adjust emission controls. This helps pumps and engines keep power during emergencies. The EPA also made new rules for diesel exhaust fluid system care. In 2025, the NHTSA will require automatic emergency braking on light vehicles. This rule may change fire truck safety features in the future.
If a fire department does not follow these rules, there are big fines. The first time, the fine is $275. If it happens again in five years, the fine can be up to $1,000. In some states, if someone gets hurt or property is damaged, it is more serious. It can lead to misdemeanor or felony charges, losing a license, or bigger fines. Fire department leaders must make sure all vehicles and crews follow nfpa rules to avoid these problems.
Maintenance Protocols
Regular care keeps fire trucks ready to go. The nfpa says drivers must check trucks every day. These checks help find problems early. Preventive care depends on how much the truck is used. Teams watch miles, engine hours, and fuel use to plan service. Brakes must be tested once a year and after any fix. The nfpa does not set one schedule for all. Each fire department must make its own plan and follow nfpa rules.
Drivers check trucks every day
Operators check trucks every week
Preventive care is based on miles, engine hours, or days
Brakes are tested every year
Fix any pump or equipment problem right away
Tip: Keeping a good maintenance log helps prove the fire department follows all the rules.
Operator Training
Operator training helps every fire truck driver stay safe. Training teaches defensive driving, pump use, and what to do in a crash. Drivers learn to drive in bad weather and on different roads. They also learn why speeding and distractions are dangerous. The nfpa says all drivers must finish these classes before driving a fire truck.
Training Module | Key Components Covered | Duration |
|---|---|---|
Distracted Driving Awareness | Risks of distractions, ways to avoid them, changes for conditions | 1 hour |
Emergency Vehicle Driving | Safe driving, crash dangers, intersection risks, backing up safely | 30 minutes |
Personnel Selection | How to pick drivers, legal rules, driving guidelines | 30 minutes |
Emergency Vehicle Characteristics | Features, checks, care, weight, and balance | 30 minutes |
Driving Dynamics | How to stop rollovers, vehicle movement, physical forces | 30 minutes |
Driving Techniques | Defensive driving, space, spotting hazards, braking | 1 hour |

Firefighters must pass all classes before they can drive a fire truck. The fire department checks training records often to make sure everyone follows nfpa rules. Good training keeps firefighters, trucks, and people safe in every emergency.
Trends in Emergency Vehicles
Technology Innovations
Emergency rescue vehicles now use new technology to help with safety and speed. Many fire trucks have artificial intelligence and robotics. These systems help crews make fast choices in hard situations. Some new fire trucks use drones to see from above. This helps teams find people and plan rescues. Robotic fire truck units can go into broken buildings or flooded streets where people cannot go.
Other new ideas include:
Smart wearables that check responder health and the air.
IoT devices, like GPS life jackets, for real-time tracking.
AI-powered systems that guess dangers and show safe routes.
Autonomous navigation uses LiDAR and computer vision to move fire trucks.
Lightweight materials, like carbon fiber, make equipment stronger and easier to use.
Pre-emptive traffic signal technology changes lights so fire trucks can pass fast and safe.
Cities like Roswell, Georgia, use these smart traffic systems at many intersections. These upgrades help fire truck crews get to emergencies faster and lower accidents. Many countries now use autonomous fire trucks and ambulances for disasters, wildfires, and city rescues.
Technology in fire truck design keeps changing. It makes emergency response safer and more efficient.
Updates in Standards
Recent changes in emergency vehicle standards help make work smoother and safer. The nfpa put many rules into single documents, like NFPA 1010 and NFPA 1970. This makes it easier for fire truck teams to find and follow safety rules. Using the same words and steps helps different fire truck crews work together.
The nfpa also made a new "Support Person" role. This person does jobs that do not need a firefighter. This lets the main crew focus on rescues. The new role helps fill volunteer spots and brings more people to emergency work. Training programs now teach these support skills. This makes fire truck work more efficient.
New detection systems, like the RT-DETR-EVD model, help spot emergency vehicles faster and better. These systems use less power and work well in busy places. The NHTSA now says all light vehicles must have automatic emergency braking by 2029. This rule will help stop crashes with fire trucks and keep everyone safer.
Updates in standards and technology help fire truck crews respond quickly and save more lives.
Emergency rescue vehicle standards help keep responders and the public safe. One important rule is NFPA 1900. It covers how vehicles are built, what equipment they need, and how to keep them safe and working well. Following these rules and using new ideas helps save lives. It lowers the chance of deadly accidents and problems with emergency vehicles.
Safety changes since 1960 have saved more than 600,000 lives.
Better driver training and risk programs can cut accidents by up to 58%.
Trusted Brands | Key Strengths |
|---|---|
Advanced technology, global trust | |
Whelen | Reliable lighting and siren systems |
Feniex | Innovative, affordable solutions |
Learning about these rules and picking good brands helps everyone stay safer during emergencies.
FAQ
What are the main standards for emergency rescue vehicles?
Emergency rescue vehicles must follow rules for safety and equipment. Standards like NFPA 1900 and CAAS GVS list these rules. These standards help keep crews and the public safe in emergencies.
Why do emergency vehicles need special lighting and sirens?
Special lights and sirens help emergency vehicles move fast in traffic. They warn drivers and people walking nearby. This helps rescue teams get to people faster and safer.
How often should emergency vehicles get maintenance checks?
Teams should check emergency vehicles every single day. Regular checks help find problems before they get worse. Scheduled care keeps vehicles ready for any emergency. Good records show teams follow all safety rules.
What equipment must an ambulance carry?
Ambulances need medical devices like oxygen systems and monitors. They also need stretchers, trauma kits, and protective gear. Storing equipment the right way keeps it safe and easy to grab.
Can emergency rescue vehicles work in rough terrain?
Many new rescue vehicles, like those from CJQC, have all-terrain features. These vehicles use strong engines and four-wheel drive. They can go through floods, mud, and rocks to help people in danger.






